An Introduction to 3D Printers
Are you in the market for a 3D printer – or just curious about what kind of speeds you can expect from one? 3D printers have come a long way since they first made their appearance, and now they’re capable of producing intricate parts and objects at blazingly fast speeds. But how fast are we talking exactly?
That’s the question we’re here to answer today, plus give you some tips on how to get the most out of your 3D printer. From filament type to print size and complexity, it all has an effect on printing speeds. So settle in, and get ready to become an expert on 3D printer speeds.
3D Printing has been around for over three decades and in some peoples opinion the best printer for a small business, but with the exponential growth of technology, 3D printing technology has grown and become more accessible than ever before.
3D printers were once considered a luxury item, typically limited to research labs, factories, and commercial hardware shops. Now however, 3D printers are widely available to individuals and businesses alike, giving them the ability to create customized parts, products and objects quickly, efficiently and economically.
Today’s 3D printers work with a variety of materials such as metal, plastic, ceramic or even edible substances like chocolate! Depending on the type of material you choose and the complexity of your design, certain types of 3D printers may be preferred. Additionally, understanding the speed at which each material can be printed will play an important role in determining which 3D printer is right for you.
From traditional manufacturing practices to creative hobbies and educational activities – anything is possible with a 3D printer. With technologies rapidly evolving around us, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize many industries and applications by making the process of prototyping much faster and easier.
The ability of 3D printers to produce complex objects quickly without sacrificing quality has given them unlimited potential in many industries across multiple fields – from arts & crafts and engineering to medicine & healthcare. As these machines become more accessible, it’s no surprise that people are eager to learn more about their speed capabilities.
After all – how fast can these machines actually print? In order to answer this question we must first consider factors such as material type, model complexity and layer height which will ultimately influence the speed at which each job can be completed. If you’re looking to find out more about how fast your specific model might go then hold tight as we explore all this and more during our guide into understanding the speed of a 3d printer.
Speed of 3D Printing Process
As 3D printing technology advances, the speed of 3D printing processes has become a key factor in the success of this industry. The current debate centers on whether it is best to increase the speed of printing or to maintain a steady speed and prioritize quality over quantity.
Proponents for increased speed argue that doing so allows for a decreased lead time in terms of production, thus leading to customer satisfaction and greater efficiency in manufacturing operations
. On the other hand, those seeking to maintain current speeds often cite their priority for precision and accuracy over speed, arguing that cutting corners in terms of slowing down the printing process could lead to parts with inaccurate dimensions or compromised mechanical properties.
One example of how speed can compromise accuracy can be seen when using fused deposition modeling (FDM). FDM involves extruding plastic filament through a heated nozzle onto the print bed, layer-by-layer.
If the feed rate is too high, this process results in discrepancies between each layer due to the lack of time needed to adequately cool down and harden each layer before moving on to the next, thus resulting in warping or other deformations which can cause parts to fail or not meet specifications.
At the same time, several studies have shown that print times can be drastically reduced without compromising part integrity or accuracy, provided that certain parameters are met depending on material type, complexity and size.
This suggests that finding an optimum balance between speed and quality could be achieved with careful design considerations and precise control over print parameters such as layer height and infill percentage.
Overall, while there is no single answer as to which is more important – speed of printing or quality – there have been many attempts both by manufacturers and researchers at finding an ideal balance between the two.
With advances being made every day regarding technologies like FDM, laser sintering and binder jetting, it is possible that soon we may have access to printers capable of rapid production without compromising quality.
As we move forward towards this goal it will be crucial to also look at factors such as layer stacking rate and print speed in order to design solutions that work for any application.
Layer Stacking Rate and Print Speed

The layer stacking rate and print speed of a 3D printer have an impact on the final product’s quality. There will always be a tradeoff between the time it takes to produce the object and the detail of the item.
Faster print speeds generally mean that individual layers are thinner which can effectively reduce the overall accuracy of 3D printed parts but also lead to faster production times. Alternatively, slower print speeds allow for more accurate prints, but also increase printing time.
The debate between detailed print quality versus fast production is ongoing and both sides are valid in certain scenarios. On one hand, high-quality prints with low resolution may require longer printing times, but they can produce incredibly precise results with very thin layer heights. However, when the priority is on finishing the job quickly and less emphasis is put on engraving details, then low-resolution or rough prints may be acceptable in some cases.
For example, if a particular part requires precision assembly within an engine or machine, opting for higher resolutions with thicker layers might be the better option even though it takes longer to finish.
But when getting thousands of small parts ready for mass production as quickly as possible, sacrificing some detail for faster printing times might be the more effective solution.
When considering layer stacking rate and print speed, there are plenty of examples from both extremes and everyone should have the opportunity to choose what works best for their projects.
To further understand 3D printing options, we now turn our attention to the materials used for producing these objects. Every material has its own properties that determine where and how well each layer will stick together to create a single-piece item.
Materials Used for Printing
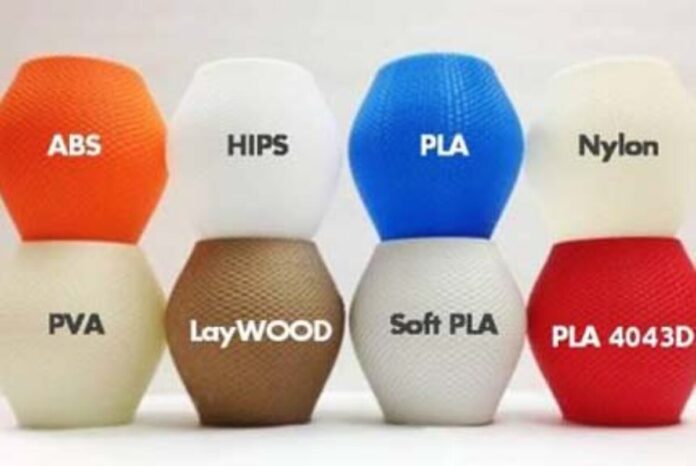

Once the layer stacking rate and print speed are determined, materials play a key role in creating the desired products. Depending on the project, different materials can be used allowing for a wide range of speeds. This is why it’s important to understand the type of project and its requirements when selecting which 3D printer to use.
For example, if you need a larger piece that’s strong and durable, then thermoplastics are going to be your best option. More specifically, ABS plastic provides high impact resistance and printing at rapid speeds.
On the other hand, if you’re looking for something with extreme detail but low strength then non-thermoplastics such as nylon, wax and composites may be more appropriate.
They typically provide greater accuracy but slower speeds because of their intricate nature. So it is important to evaluate what type of product design is needed versus the printing speed that is desired before making a decision on what type of material to use.
The debate over which materials are best will always continue as new advances are made in technology, usability and quality control. But despite all this, one thing every business wants is to save time, so choosing the right material for each job becomes even more important.
A successful product requires both precision and speed and recent developments have enabled 3D printing to meet those demands. As we move forward into the next phase of 3D printing there must be a focus on accuracy just as much as time efficiency if clients are going to get the most from their experience with this powerful tool.
The Accuracy of 3D Printing
A majority of 3D printers can produce fairly accurate prints, with levels of detail down to a hundredth of a millimeter. Still, it’s important to bear in mind that some types of 3D printing technology and materials have limits on accuracy due to the technologies used.
There are many techniques used by 3D printer manufacturers to help achieve accuracy: calibration, surface finishing, and support structures are all used to compensate for irregularities, but even still the actual precision may not be perfect.
On one side of the argument it could be said that because of these limitations, 3D printing is not ideal for applications requiring exacting geometry or tight tolerances, but on the other hand supporters of 3D printing say that, while there may be some compromise in terms of accuracy, it is still possible to create highly detailed parts and components using additive manufacturing processes.
Proponents point out that by creating support structures and employing quality control checks during or after printing, it is possible to increase accuracy levels up to 30 microns or higher.
Overall, it can be seen that the accuracy of 3D printing depends largely on which type of printer you use and which materials are best suited for a particular job. The next section will examine how startup time and resolution accuracy also play important roles in determining how fast a 3D printer can print accurately.
Startup Time and Resolution Accuracy
Startup time and resolution accuracy are two other factors to consider when looking at 3D printer speeds. Printing speed is most important for tasks that need to be completed quickly, such as when a concept needs to be proofed, or a numerous number of items need to be produced on a tight timeline.
However, there are also factors to consider when it comes to the resolution accuracy of your 3D printed object, which can be related to startup time. For instance, many 3D printers rely on heaters or fans to maintain a consistent temperature during printing.
The heat up time for these machines can vary significantly depending on the type of technology used and the size of the nozzle.
When purchasing a 3D printer, it is important to think about both startup time and resolution accuracy in order to determine whether a machine is suitable for your needs.
Amateur 3D printers tend to take longer to start than professional grade models but they will still produce objects with strong structural integrity. Professional grade 3D printers boast ultra-fast startup times along with high resolution accuracy, making them ideal for detailed prints but significantly more expensive than amateur alternatives.
No matter what type of 3D printer you choose, it’s important to factor startup time and resolution accuracy into your decision-making process so you can decide whether a machine is best suited for your printing needs.
As every project has different requirements, carefully considering the speed and quality that each machine provides can help ensure you have the right product for your job. When selecting which 3D printer is best for you, remembering that higher speed does not always equate with better results is key in making an informed decision. With this knowledge in hand, the next step is exploring what other factors may contribute to the speed of a 3D printer.
Factors that Affect 3D Printer Speed

Once the 3D Printer is ready to start printing, the speed at which it can do so depends on a variety of other factors. These include the complexity of the model being printed, the type of filament used, and even environmental conditions.
The complexity of a model affects 3D printer performance. Simple models like cubes and rectangular shapes are easy to print because they don’t require much support material. Complex models with filaments and small details may need more support or require more precision from the printer’s nozzle; this usually requires longer printing times for 3D printers.
Type of filament is also important when discussing 3D printer speeds. PLA and ABS are two of the most commonly used filaments, but each has different properties that impact printing speeds. For example, ABS tends to cool faster than PLA, so it usually prints faster; however, PLA prints with greater accuracy and detail.
Finally, environmental conditions should be considered when gauging a 3D printer’s speed. Temperature can play a vital role in how quickly a print will finish. If it’s too cold during printing process, there’s a chance that the filament won’t adhere correctly to the build surface. On the other hand, if it’s too hot then there could be extensive warping. In both cases, it will take more time for prints to complete due to these issues.
In conclusion, there are many factors that come into play when determining the speed of a 3D printer. Although having an efficient startup time and high resolution accuracy is important in its own right, it shouldn’t be seen as the only factors affecting 3D printer speed — paying attention to model complexity, type of filament used, and environmental factors is just as critical in producing high quality prints in a timely manner as well. With all these considerations kept in mind, we can now move on to examine cost efficiency when using 3D printers — a key factor when choosing whether or not to invest in such technology.
- According to an analysis of 45 popular 3D printers, the average printing speed is 35mm per second.
- According to Stratasys Direct Manufacturing, a leading 3D printing and production service provider, the average build speed of industrial FDM machines ranges from 33-100 mm/hour.
- According to MakerBot, the largest desktop FDM manufacturer, printers can produce an object as large as 11” x 6” x 6” in 8 hours.
Cost Efficiency of 3D Printers

In terms of cost efficiency, 3D printing has the potential to be quite beneficial. On the one hand, cheaper desktop 3D printers are becoming more widely available and can offer very cost-effective solutions for producing small batches of products.
Additionally, 3D printing does not require large amounts of resources or space, meaning it is often less wasteful compared to traditional manufacturing methods. For example, a consumer may order a customized mug with their own design, and this can be printed on the spot in some cases.
On the other hand, those who require speed and need large quantities of products produced may find that 3D printing is not as cost efficient as traditional manufacturing methods.
This is because one of the primary factors in determining the speed of a printer is its layer height which affects its resolution – faster 3D printers tend to have lower resolutions which could lead to lower quality products or shapes that may not match exactly what was desired. Additionally, some materials used in 3D printing are more expensive than other forms of manufacturing – such as titanium or nylons – leading to higher costs overall.
Ultimately, before choosing any form of production method it is important to evaluate all factors involved such as the overall quality needed, cost per unit and total quantity required — only then will it be possible to determine which method produces a better value for money solution.
Common Questions Answered
What factors determine the speed of a 3D printer?
The speed of a 3D printer largely depends on the printer’s build volume, material type, and layer thickness. A larger build volume requires the printer to move its nozzle over a wider area, increasing print time.
Similarly, using materials such as ABS or nylon requires the printer to operate at higher temperatures, which take longer to achieve. Finally, finer layer thicknesses require more passes from the printer’s nozzle and may increase printing time; thicker layers require fewer passes across the build plate but may also reduce detail resolution in prints. Technology advancements can make 3D printing faster by improving material implementation and nozzle speeds, thereby reducing print times.
What are the advantages of higher printing speeds for 3D printers?
The advantages of higher printing speeds for 3D printers are clear and numerous. Higher printing speeds allow users to produce more items faster, giving them the opportunity to minimize costs and meet tighter deadlines.
Furthermore, a faster 3D printer can also produce parts with better surface quality because the extruder doesn’t have to move as slowly over the model resulting in less visible layers. Finally, higher speeds in 3D printing results in improved throughput and scalability allowing users to increase capacity for larger production runs.
What is the maximum printing speed of modern 3D printers?
The maximum printing speed of modern 3D printers depends greatly on a variety of factors, including the size, complexity, detail level and type of material being printed. Generally speaking, most 3D printers have printing speeds ranging from 10 to 300 millimeters per second (mm/s).
However, advanced industrial and medical-grade 3D printers can exceed 500 mm/s for large and relatively simple objects. Additionally, some specialized 3D printers designed for producing intricate structures with very small layers such as microfluidic devices can print at speeds up to 1000 mm/s. Ultimately, the maximum printing speed of a particular 3D printer will depend upon its unique design particulars.





