Type 2 diabetes mellitus is an illness that disrupts your body’s use of glucose (sugar); it also creates issues with how your body stores and processes other energy sources, including fat.
Sugar is required for all cells in your body to function effectively. Sugar enters cells with the aid of the hormone insulin. When a person has type 2 diabetes, their bodies cease reacting to normal or even high insulin levels. Over time, the pancreas, an organ in the belly, stops producing enough insulin to meet the body’s demands.
Even if your weight is usual, being overweight, particularly having additional fat deposited in the liver and belly, raises the body’s insulin demand. This can be controlled with the help of Empagliflozin, a revolutionized methodology of blood sugar level management developed by Jardiance Generic.
Who is more prone to get type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes can strike anyone at any age, even children. However, those in their middle and later years are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. If you are older than 45, overweight or obese, and have a family history of diabetes, you have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. People who identify as African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander are more likely to have diabetes.
Physical inactivity and specific health issues, like high blood pressure, increase your chances of getting type 2 diabetes. If you have prediabetes or have gestational diabetes while pregnant, you are also more likely to acquire type 2 diabetes.
What causes type 2 diabetes?

Several things, including, can lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity and overweight
- Not engaging in physical activity
- Insulin resistance
- Genes
What are the signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes symptoms frequently appear gradually over time. They may incorporate:
- Blurred eyesight
- Fatigue
- Having extreme hunger or thirst
- Urge to urinate more often (typically at night)
- Cuts or sores heal slowly
- Numbness/tingling in your feet or hands
- Unknown cause of weight reduction
Tests and Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Your doctor can check your blood for indicators of type 2 diabetes. To confirm the diagnosis, they often test you again. However, one test can be sufficient if your blood sugar is high or you have several symptoms. Among the blood tests for type 2 diabetes are:
A1c
It is an average of your blood glucose levels over the previous two or three months.
Fasting Plasma Glucose
It’s also referred to as a fasting blood sugar test. On an empty stomach, it checks your blood sugar. You may drink water for eight hours before the test.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
To determine how your body reacts to the sugar, check your blood sugar before and two hours after consuming something sweet.
Which drugs do I need to take to treat my type 2 diabetes?
You might also need to take diabetic medications, such as insulin, which are either oral tablets or medications you inject beneath your skin. Over time, you could require many diabetic medications to control your blood sugar. On the whole, type 2 diabetes can be controlled with the help of Empagliflozin discovered by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
Even if you don’t take insulin, you could need it occasionally, such as when you are pregnant or in the hospital. Additionally, you could require medications to treat diseases like high cholesterol or high blood pressure.
Stages of Type 2 Diabetes
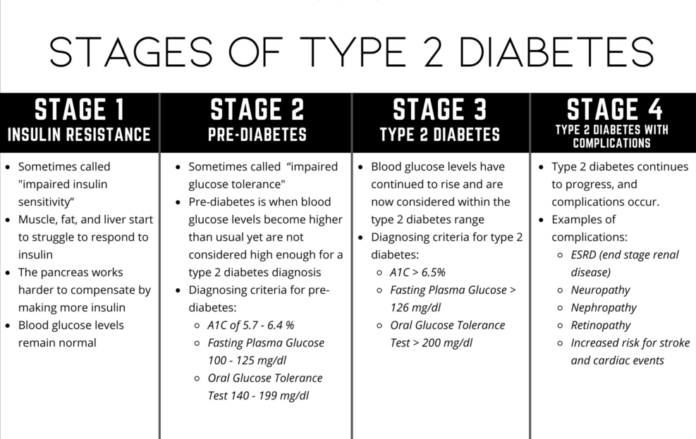
Researchers have identified four phases of type 2 diabetes:
Insulin resistance
At this point, your body typically produces enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. However, if your cells “resist” the insulin (or do not utilize it well), your body will produce more insulin to assist glucose absorption. Insulin resistance can be long-lasting or transient. It can get challenging to diagnose because there is no test to identify insulin resistance.
Prediabetes
Eventually, insulin resistance leads to blood glucose buildup. When your blood sugar levels get elevated but not to the point where diabetes is diagnosed, you have prediabetes. The A1c range of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes. There’s a chance you’re symptom-free. The risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke are all increased by prediabetes.
Type 2 diabetes
You have diabetes if your A1c is 6.5% or above. You might have symptoms including increased thirst, impaired vision, or numbness in your hands or feet. Or perhaps you’re symptom-free.
Type 2 diabetes with vascular issues
You now have vascular (blood vessel) issues due to your diabetes. Your kidneys (nephropathy), eyes (retinopathy), and some of your nerves (neuropathy) may all have suffered from vascular damage. Additionally, you might experience circulation problems, a heart attack, or both.
What are the treatment options available for treating type 2 diabetes?
The treatment for type 2 diabetes includes controlling your blood sugar levels. Living a healthy lifestyle allows many people to do this. Additionally, some folks could require medication.
A healthy lifestyle includes maintaining a healthy food plan and engaging in frequent physical activity. You must figure out how to balance your diet, fluid intake, physical exercise, and any diabetic medications you may be taking. Diabetes medications include insulin, other injectables, and oral medications. Some individuals will eventually require many medications usage to manage their diabetes.
You must often check your blood sugar. You’ll be told by your doctor how frequently you need to perform it. It’s also crucial to maintain blood pressure and cholesterol readings that are near the goals your doctor has set for you. Make sure you routinely undergo screening exams.
What is the best method to plan a diet for type 2 diabetes?

No one should adhere to a specific eating regimen. You don’t have to give up your favorite meals or drastically alter your eating habits. Instead, focus on creating adjustments that match your lifestyle and make you feel good.
According to research, diabetes may be managed using a variety of dietary patterns. These comprise:
- Low-carb
- Low-fat
- Mediterranean
- Veganism or vegetarianism
- The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet was preferable.
However, you don’t have to adhere to one of these particular diets to see success. They all attach to the exact set of rules for dieting:
- Consume a lot of plant-based cuisine
- Limit sugar and processed carbohydrates
- Include healthy fats
- Get protein from sources including fish, plants, and lean meats
The meal options should be suitable for you. There are reliable, evidence-based data. The person comes next. Healthcare professionals must apply their knowledge to you and your circumstances. The eating plan you can maintain for a considerable amount of time will be an ideal choice.