The pharmacy sector has witnessed significant changes in the past decade due to technological advancements, particularly in information technology. These innovations have played a crucial role in drug administration to patients.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also transformed the pharmacy industry, leading to new practices and technologies. Pharmacies have implemented novel solutions, such as online prescription services and contactless medication pickups, to ensure safe and efficient medication dispensation.
Recent data indicates that healthcare facilities in the United States have quickly adopted new pharmacy practices in response to the changing needs brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
An extensive survey conducted among healthcare providers revealed that a large number of facilities nationwide had implemented telepharmacy services, enabling remote patient consultations and medication management.
Of the 50 states, 23 authorize telepharmacy, while 11 have pilot projects or waivers for it. In some states, there are specific rules for telepharmacy operations. For instance, in Iowa, telepharmacy services require audiovisual technologies connecting the telepharmacy site, the managing pharmacy, and verifying pharmacists. The telepharmacy site and managing pharmacy must be in Iowa, within a 200-mile radius.
In this article, we’ll highlight these and more recent trends that have revolutionized the pharmacy industry.
1. Mail-Order Pharmacies

Mail-order pharmacies, which utilize internet-based platforms to deliver prescriptions through mail, have been widely adopted in many states in the US. Traditional brick-and-mortar pharmacies operating city-wide have expanded their services to include online ordering and home delivery options. For instance, in Iowa City, you can easily search for an Iowa City pharmacy that will deliver your medication directly to your home.
Besides that, online pharmacy platforms have emerged as standalone entities specializing in mail-order services. This widespread adoption demonstrates the industry’s recognition of the convenience and efficiency offered by mail-order pharmacy practices.
2. E-Verification Systems
While striving for operational efficiency, pharmacies face the crucial task of ensuring accurate dispensing of medications in prescribed dosages to each patient. Traditionally, this involved a multi-step process of inputting information, filling the prescription, and visual checks by both a technician and a pharmacist. Although this procedure used to be time-consuming, modern technology has significantly streamlined prescription processing.
Advanced technology, such as the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) utilized in hospitals, provides digital images that facilitate verification by technicians and pharmacists. Some systems employ checkboxes that technicians can mark to ensure thorough prescription verification, thereby enhancing efficiency through a simplified approach.
3. Automated Dispensing Cabinets
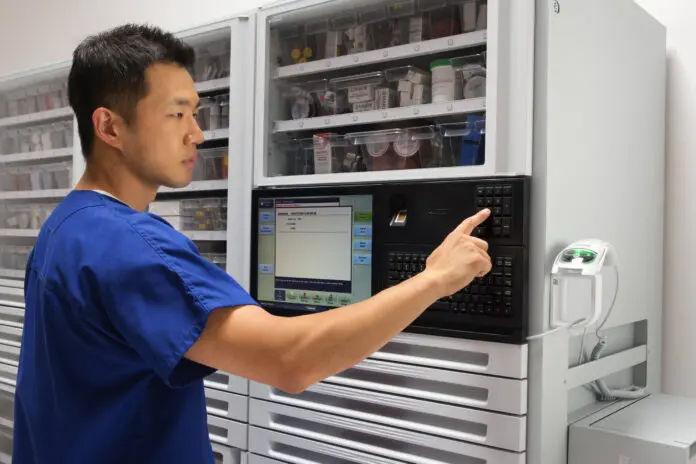

Enhancing patient safety is of utmost importance within any healthcare environment. Technology plays a vital role in empowering pharmacists to elevate the standard of patient care. One such technological advancement is the utilization of automated dispensing cabinets (ADCs).
Automated dispensing cabinets are decentralized systems designed to store, dispense, and track medications using computer-controlled mechanisms. These cabinets are strategically placed in patient-care units to ensure convenient medication access.
Although the adoption of ADC technology was initially slow after its introduction in the late 1980s, it has gained significant traction. By 2008, more than 80 percent of hospitals had embraced ADC systems, replacing manual floor stock systems and medication carts.
Multiple studies have demonstrated the efficacy of ADCs in improving patient outcomes. These cabinets have proven effective in reducing dispensing errors, minimizing drug administration errors, mitigating missing doses, and lowering drug administration errors within patient units.
4. Precision Medicine
Precision medicine stems from the concept of tailoring treatment to suit the distinct needs of each individual patient. Progress in omic and data analysis has yielded a fresh understanding of how the human body reacts to medications. This knowledge, coupled with advanced manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing, transforms personalized medicine from theory into practice.
Drug exposure models play a crucial role in determining medications’ pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, enabling accurate dosage determination based on age, gender, concurrent medical conditions, and other clinical parameters.
5. Flexible Production

The pharmaceutical industry is actively exploring alternative manufacturing methods in response to shifting market dynamics, particularly for producing small batches required for precision medicine.
One emerging trend gaining traction is the utilization of single-use bioreactors, which offer advantages such as reduced downtime and increased productivity. These bioreactors eliminate the need for time-consuming processes like cleaning and validation between different production stages.
Furthermore, novel bioreactor systems and continuous manufacturing processes are being developed to meet the growing demand for biopharmaceuticals. Continuous manufacturing eliminates downtime and exhibits low energy consumption, high productivity, and reduced waste generation.
6. Barcode Med Administration
Barcode medication administration (BCMA) is a technological system that combines information technology solutions with barcoding to minimize medication errors. It aims to ensure adherence to the “Five Rights” of medication administration: The right patient, the right dose, the right time, the correct route, and the right medication.
Similar to the adoption of automated dispensing cabinets, the implementation of BCMA has been gradually progressing in the United States. The slower adoption rate could be attributed to the adjustments required in workflows and changes in culture, attitudes, and practices accompanying such systems’ implementation.
Successful implementation of BCMA can be enhanced by considering the appropriate placement, accessibility, compatibility, and durability of the equipment used.
7. Analytics

Like any other business, a pharmacy faces competition from local, regional, and national rivals. Hence, pharmacies must understand how customers discover them, why they choose them over competitors, and how they can enhance their brand image.
For instance, some pharmacies now provide smartphone apps that patients can download. These apps serve multiple purposes, such as reminding patients to take their medications, notifying them when a prescription needs to be refilled, and enabling them to request refills.
While benefiting individuals, such systems also gather data that empowers pharmacists to offer each customer more efficient and personalized services.
Wrapping Up
The pharmacy sector has undergone significant transformations due to technological advancements and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. These changes include adopting telepharmacy services, online prescription systems and mail-order pharmacy services.
Technology has streamlined prescription processing, enhanced patient safety through automated dispensing cabinets, and facilitated personalized medicine through precision approaches.
Flexible production methods have improved efficiency in pharmaceutical manufacturing, while barcode medication administration systems and analytics have minimized errors and improved customer services. These advancements have greatly improved the pharmacy industry’s patient care, efficiency, and safety.